1. What is PHP?
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a server-side scripting language used primarily for web development. It is an open-source language that can be embedded into HTML and is used to create dynamic web pages and web applications.
PHP is a popular programming language for web development due to its ease of use and flexibility. It can interact with databases, handle form data, generate dynamic page content, and more. PHP code is executed on the server-side, which means that it runs on the web server rather than the user's computer. This allows developers to create dynamic and interactive web pages that can be customized based on user input or other factors.
PHP is supported by most web hosting providers and is used by many popular websites, including Facebook, Wikipedia, and WordPress.
2. What are the difference between variables and constants in PHP ?
In PHP, variables and constants are both used to store values, but they differ in terms of their mutability and usage. Here's a brief comparison between variables and constants in PHP:
Variables:
A variable is a container that holds a value, such as a string or number, and the value can be changed during the execution of a script.
In PHP, variables are defined using the dollar sign ($), followed by the variable name, and then assigned a value using the assignment operator (=).
For example: $name = "John"; $age = 30;
Constants:
A constant is a named value that cannot be changed during the execution of a script.
In PHP, constants are defined using the "define" function, and the value is assigned to the constant at the time of its definition.
For example: define("PI", 3.14); define("APP_NAME", "My App");
So, the main differences between variables and constants in PHP are that variables can be changed during the execution of a script, whereas constants cannot be changed, and constants are defined using the "define" function, while variables are defined using the dollar sign.
3. What is PEAR?
PEAR stands for "PHP Extension and Application Repository". It is a framework and distribution system for reusable PHP components, including libraries, modules, and tools. PEAR provides a standard way for PHP developers to share and reuse code, and simplifies the process of installing and managing PHP packages.
4. What is the difference between static and dynamic websites?
Static websites are those where the content is fixed and doesn't change unless the website owner manually updates it. They are usually built using HTML, CSS, and possibly some JavaScript, and are typically faster and simpler to create and host than dynamic websites. However, they can be less flexible and less interactive than dynamic websites.
Dynamic websites, on the other hand, are built using server-side programming languages (such as PHP, Python, or Ruby) and a database to create content that can change based on user input, user preferences, or other factors. They can be more complex and time-consuming to develop and host than static websites, but they offer more flexibility, interactivity, and personalization options for the user. Dynamic websites often use content management systems (CMS) to make it easier to create and manage website content.
5. Is PHP a case sensitive language?
Yes, PHP is a case sensitive language, meaning that it distinguishes between uppercase and lowercase letters. This means that variables, function names, and other identifiers in PHP are case sensitive. For example, the variable $myVar is different from the variable $myvar, and a function named myFunction is different from one named myfunction. It is important to use consistent casing when using identifiers in PHP code to avoid errors and confusion.
6. What are the popular frameworks in PHP?
There are several popular PHP frameworks that are widely used for web development. Some of the most popular ones are:
Laravel: A powerful and elegant framework that emphasizes expressive syntax and conventions, and provides features like routing, database migrations, and queue management.
Symfony: A robust and flexible framework that is designed to support large-scale enterprise applications, and includes components for templating, security, and form generation.
CodeIgniter: A lightweight and fast framework that is easy to learn and use, and includes features like database access, form validation, and error logging.
CakePHP: A full-stack framework that provides a structured way to build web applications, with features like authentication, caching, and database access.
Zend Framework: A modular and extensible framework that provides a wide range of components for building web applications, including authentication, caching, and database access.
These frameworks can help speed up development and improve code quality by providing pre-built components, conventions, and best practices. Each framework has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it's important to choose the one that best suits your needs and skill level.
7. What are the different types of loop in PHP?
In PHP, there are four different types of loop structures that can be used to repeat a block of code. They are:
for loop: A for loop is used to execute a block of code a fixed number of times. It consists of three parts: initialization, condition, and increment/decrement.
while loop: A while loop is used to execute a block of code repeatedly as long as a condition is true. It only has a single condition.
do-while loop: A do-while loop is similar to a while loop, but it executes the code block at least once before checking the condition.
foreach loop: A foreach loop is used to loop through arrays and objects. It executes a block of code for each element in the array or property in the object.
These loop structures provide a powerful way to repeat code, and are often used to process arrays or other collections of data. It's important to use loops carefully, though, as they can be resource-intensive and slow down your code if not used correctly.
8. How can PHP and HTML interact?
PHP can be embedded in HTML code to create dynamic web pages that can respond to user input and interact with databases and other web services. This is done using PHP code blocks, which are delimited by tags, and can be inserted anywhere in an HTML document.
For example, the following code block uses PHP to output the current date in an HTML document:
.png)
When this code is executed by a web server, the PHP code block is processed and the output of the date() function is inserted into the HTML document. This allows the web page to display the current date at the time it is accessed.
In addition to outputting data, PHP can also process form data, access databases, and interact with web services. This makes it a powerful tool for creating dynamic and interactive web pages.
9. What is parser in PHP?
In PHP, a parser is a program or module that is responsible for analyzing and interpreting PHP code. The parser takes raw PHP code as input and produces a structured representation of the code that can be executed by the PHP engine.
The PHP parser is responsible for converting the text-based PHP code into a syntax tree, which is a hierarchical representation of the code that can be easily processed by the PHP engine. The parser performs several important tasks, including:
Tokenizing the input code: The parser breaks the input code into a sequence of tokens, which are the basic building blocks of the PHP language. This allows the parser to identify keywords, variables, and other language constructs.
Checking the syntax: The parser verifies that the input code follows the syntax rules of the PHP language. If the code contains syntax errors, the parser generates an error message that describes the problem.
Building the syntax tree: The parser constructs a tree-like representation of the code, where each node represents a language construct such as a function call, a loop, or a conditional statement.
Once the parser has constructed the syntax tree, the PHP engine can execute the code by traversing the tree and executing the appropriate actions for each node. The parser is an essential component of the PHP runtime, and plays a critical role in making PHP a powerful and flexible language for web development.
10. What are the different types of Array in PHP?
In PHP, there are three types of arrays:
Indexed arrays: An indexed array is a simple list of values that are stored in consecutive numeric indexes, starting from 0. The values in an indexed array can be of any data type, and can be accessed using their numeric index.
Associative arrays: An associative array is a collection of key-value pairs, where each key is a unique string and each value is associated with that key. The values in an associative array can be of any data type, and can be accessed using their key.
Multidimensional arrays: A multidimensional array is an array that contains one or more arrays as its elements. This allows you to create arrays that have more complex structures, such as tables or matrices. A multidimensional array can be either indexed or associative.
Here's an example of each type of array:
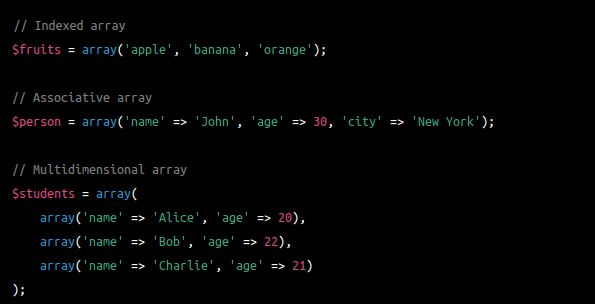
Arrays are a fundamental data structure in PHP, and are used extensively in web development to store and manipulate data. Understanding the different types of arrays and how to work with them is an important part of learning PHP.
11. What are the types of error in PHP?
In PHP, there are three types of errors:
Syntax errors: Syntax errors occur when the PHP parser encounters invalid code. These errors typically occur when there is a missing or incorrect character, such as a missing semicolon, a missing parenthesis, or a misspelled keyword. Syntax errors prevent the code from running, and are usually detected at the time the code is executed.
Runtime errors: Runtime errors occur when the code is executed and an error condition is encountered. These errors can occur for a variety of reasons, such as trying to use a variable that has not been defined, attempting to divide by zero, or passing an invalid argument to a function. Runtime errors can be detected using error handling functions like try...catch or set_error_handler().
Logical errors: Logical errors occur when the code runs without producing any errors, but the results are not what was expected. These errors can be difficult to detect and fix, and are often caused by errors in the program's logic. Debugging tools like Xdebug can help to identify and fix logical errors in PHP code.
It is important to handle errors properly in PHP code to ensure that the code runs correctly and does not produce unexpected results. Techniques like error logging, error reporting, and exception handling can be used to detect and handle errors in PHP code.
12. How to handle PHP error?
In PHP, there are several techniques for handling errors:
Error reporting: PHP provides the error_reporting function, which controls the level of error reporting. By setting the error reporting level to E_ALL, all types of errors will be displayed, including warnings and notices. This is useful during development, but should be turned off on production servers.
Exceptions: Exceptions provide a structured way to handle errors in PHP. By using try...catch blocks, you can catch and handle exceptions that are thrown by your code. Exceptions can be used to handle both runtime errors and logical errors.
Logging: PHP provides the error_log function, which allows you to write error messages to a log file. This is useful for debugging errors that occur on a production server, where error messages may not be displayed to the user.
Error handling functions: PHP provides several functions for handling errors, including set_error_handler and set_exception_handler. These functions allow you to define custom error and exception handling functions that can be used to handle errors in your code.
In general, it is a good practice to handle errors in PHP code, and to provide informative error messages to users in a way that does not compromise the security of the application. By using a combination of error reporting, exceptions, logging, and custom error handling functions, you can ensure that your PHP code is robust, reliable, and secure.
13. What is break and continue in PHP?
In PHP, break and continue are control structures used to alter the flow of execution in loops.
break is used to exit a loop early. When break is encountered inside a loop, the loop is immediately terminated and control is transferred to the statement following the loop. break can be used with any type of loop in PHP, including for, foreach, while, and do-while loops.
Here's an example of using break to exit a while loop:

continue is used to skip the current iteration of a loop and move on to the next iteration. When continue is encountered inside a loop, the remaining statements in the loop body are skipped and control is transferred back to the top of the loop to begin the next iteration.
Here's an example of using continue to skip odd numbers in a for loop:
.png)
break and continue are useful control structures for manipulating the flow of execution in loops, and can be used to write more efficient and readable code.
14. What is the difference between the include() and require() in PHP ?
In PHP, both include() and require() functions are used to include files in a PHP script. The main difference between the two functions is in the way they handle errors:
include(): If the file being included by the include() function cannot be found or loaded, PHP will generate a warning message, but the script will continue to run. The include() function is often used to include files that are not critical to the script's operation.
require(): If the file being included by the require() function cannot be found or loaded, PHP will generate a fatal error and the script will terminate. The require() function is often used to include files that are critical to the script's operation.
Here's an example of using include() and require() to include a file in a PHP script:
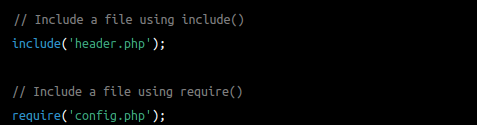
In general, it is good practice to use require() for files that are critical to the operation of the script, such as configuration files or libraries, and to use include() for files that are not critical, such as template files or utility functions. Additionally, it is important to ensure that files are included using the correct file path and that file permissions are set correctly to prevent security vulnerabilities in the PHP script.
